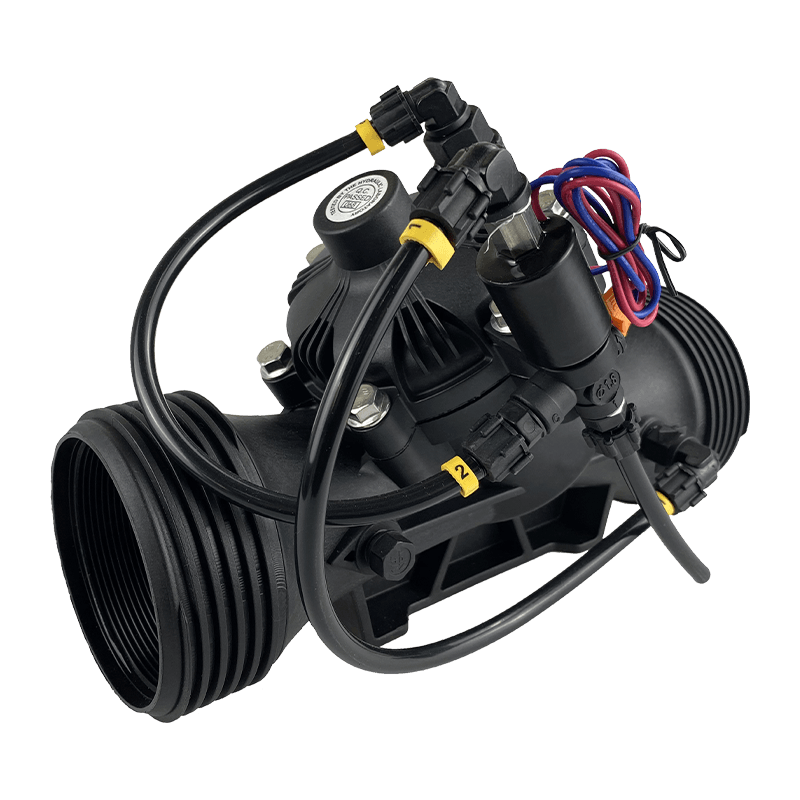
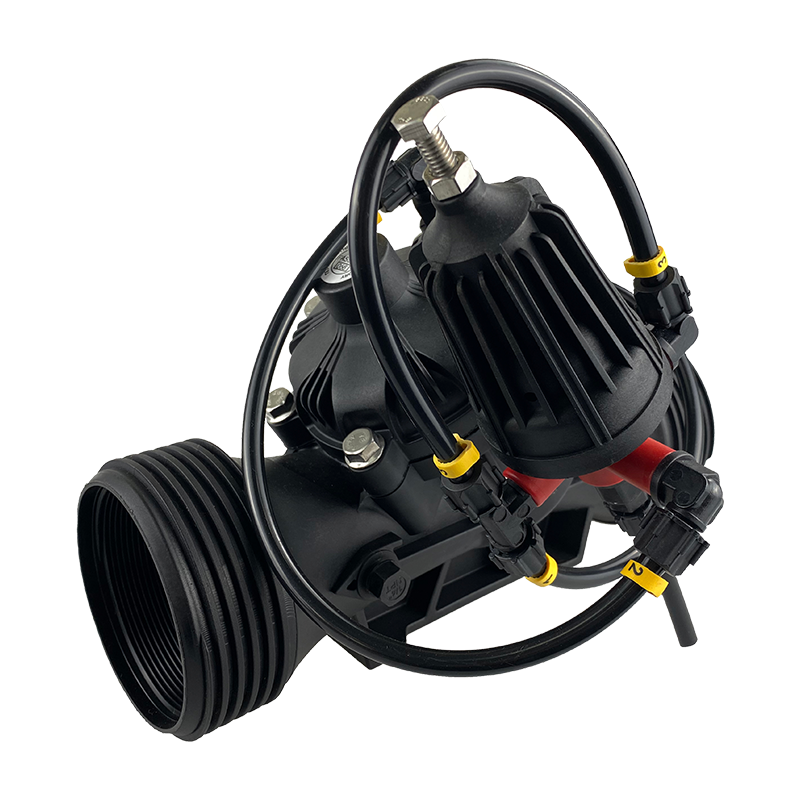
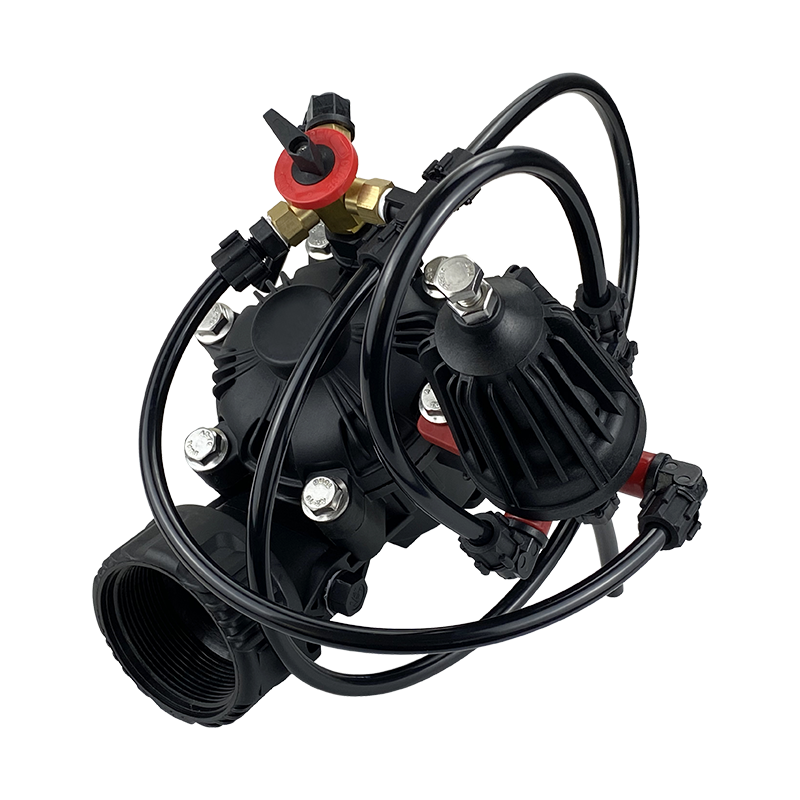
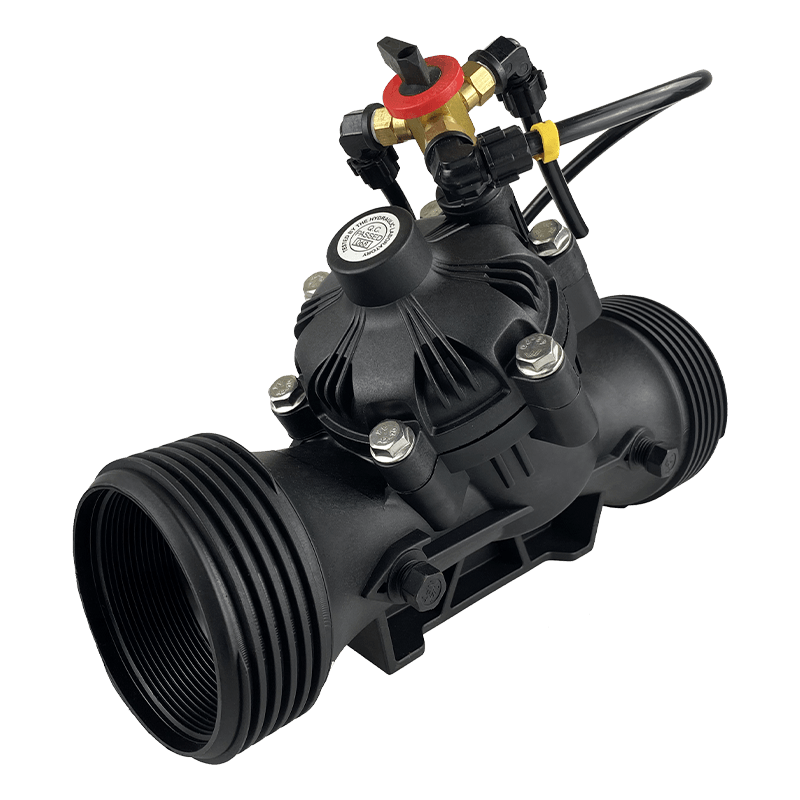
Are Smart Spray Bodies the Future of Precision Watering in Agriculture?
The question of whether smart
spray bodies represent the future of precision watering in agriculture is an interesting one, and several factors contribute to the potential significance of this technology:
Precision Agriculture Trends:The agricultural industry is increasingly adopting precision agriculture techniques to optimize resource use. Smart spray bodies align with this trend by providing real-time data and control, allowing farmers to tailor irrigation precisely to the needs of their crops.
Data-Driven Decision Making:Smart spray bodies can collect and process data related to soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop requirements. This information enables farmers to make informed decisions about when and how much to irrigate, improving overall water efficiency and crop yield.
Automation for Efficiency:Automation is a key aspect of smart spray bodies. These devices can be integrated into automated irrigation systems that respond to data inputs without manual intervention. This level of automation saves time and resources while ensuring that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time.
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI):Smart
spray bodies can facilitate Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI), a technique that adjusts the rate of water application based on the specific needs of different areas within a field. This targeted approach to irrigation can conserve water and optimize crop health.
Water Conservation Goals:As water scarcity becomes a global concern, technologies that contribute to water conservation are gaining importance. Smart spray bodies, by delivering water precisely where and when it is needed, can play a crucial role in meeting water conservation goals in agriculture.
Integration with Farm Management Systems:Smart spray bodies can be integrated into broader farm management systems. This integration allows for centralized monitoring and control, streamlining overall farm operations and providing a comprehensive view of irrigation practices.
Adaptability to Environmental Changes:Smart spray bodies can adapt to changing environmental conditions in real time. For example, they can adjust irrigation schedules based on sudden weather changes, ensuring that crops receive optimal irrigation under dynamic conditions.
Energy Efficiency:Some smart spray systems are designed for energy efficiency, utilizing solar power or low-energy technologies. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also makes these systems more sustainable and cost-effective for farmers.
While the adoption of smart spray bodies in agriculture is growing, challenges such as initial investment costs and the need for reliable connectivity in rural areas must be addressed. As technology advances and these challenges are overcome, smart spray bodies are likely to play an increasingly important role in the future of precision watering in agriculture.
In what ways do low-pressure spray bodies address water conservation challenges in urban landscaping and green spaces?
Low-pressure
spray bodies address water conservation challenges in urban landscaping and green spaces in several ways:
Reduced Overspray:Low-pressure spray bodies are designed to operate at lower pressure levels, which helps minimize overspray. By delivering water more precisely to the target areas, these spray bodies reduce water waste and prevent water from being distributed to non-essential zones.
Minimized Drift:Low-pressure systems are less prone to wind drift, where water is carried away from the intended target due to high-pressure sprays. This feature is particularly important in urban areas where wind can be a significant factor. Minimizing drift ensures that water reaches the intended plants and doesn't contribute to water wastage.
Improved Water Distribution Uniformity:Low-pressure spray bodies often feature advanced nozzle designs that promote more uniform water distribution. This ensures that each plant or area receives an adequate amount of water, reducing the likelihood of underwatering or overwatering specific zones.
Enhanced Soil Absorption:Low-pressure irrigation allows water to be applied at a rate that the soil can effectively absorb. This prevents runoff and promotes better penetration into the root zone of plants, increasing the efficiency of water use in landscaping and green spaces.
Watering Efficiency in Shaded Areas:Low-pressure systems are suitable for irrigating shaded areas where wind may not be as significant. In such areas, the risk of overspray and water drift is reduced, allowing for efficient watering without unnecessary water loss.
Integration with Drip Irrigation:Low-pressure spray bodies can be part of integrated irrigation systems that include drip irrigation. Drip systems provide water directly to the base of plants, minimizing surface evaporation and reducing water loss. Combining low-pressure sprays with drip irrigation enhances overall water conservation efforts.
Smart Irrigation Control:Many low-pressure spray systems can be integrated into smart irrigation controllers. These controllers use data on weather conditions, soil moisture levels, and plant requirements to optimize irrigation schedules. By incorporating smart technology, low-pressure systems contribute to water conservation by avoiding unnecessary watering during periods of rainfall or when soil moisture is sufficient.
Compliance with Water Use Regulations:In some urban areas, there may be regulations or restrictions on water usage. Low-pressure spray systems can help landscape managers and homeowners comply with these regulations by ensuring efficient and conservative water use.
Economic Watering Practices:Low-pressure systems often result in economic water use. By delivering water precisely where it is needed, these systems reduce water bills for both individual homeowners and municipalities responsible for maintaining urban green spaces.
Overall, low-pressure
spray bodies contribute to sustainable water management practices in urban landscaping by addressing common challenges associated with water conservation and efficiency.

 cn
cn English
English